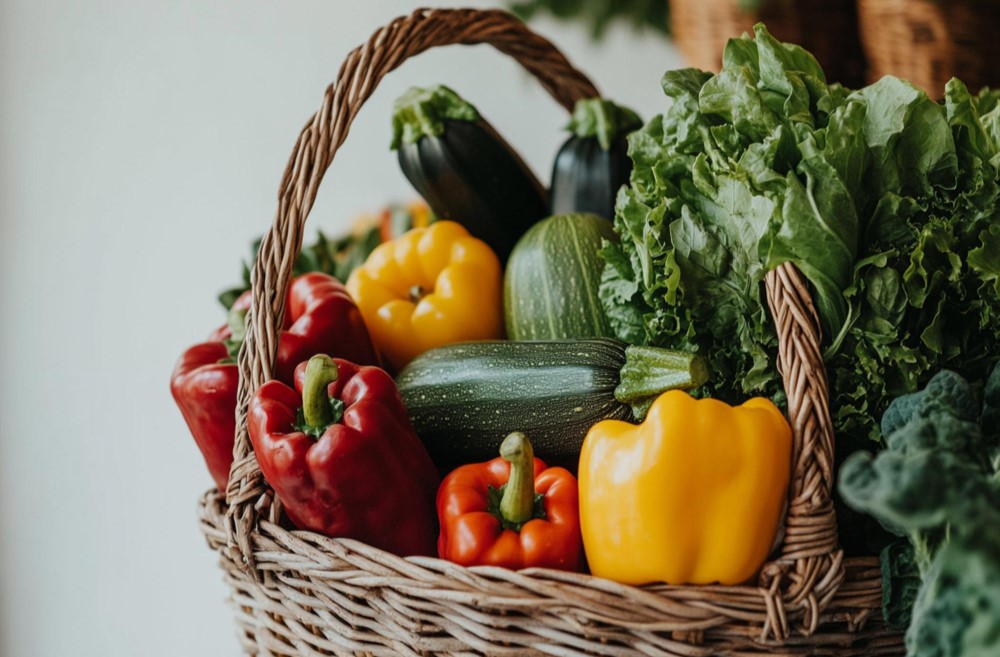
Non-starchy vegetables are a group of nutrient-dense foods low in carbohydrates and calories, making them beneficial for balanced diets and specific dietary needs. Unlike starchy vegetables, which include options like potatoes, corn, and peas, non-starchy vegetables have fewer carbs and calories, making them ideal for weight management, blood sugar control, and overall health. Examples of non-starchy vegetables include leafy greens, bell peppers, cucumbers, and mushrooms, each offering essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
These vegetables are high in fiber, supporting digestion, gut health, and creating feelings of fullness without adding significant calories. The vitamins and minerals—such as vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium, and folate—enhance immune function, skin health, and cardiovascular well-being, making non-starchy vegetables nutrient powerhouses that benefit overall health.
Why choose Non-starchy vegetables over starchy options?
A primary reason for choosing non-starchy over starchy vegetables is their low glycemic index (GI), which means they don’t spike blood sugar levels quickly, making them especially suitable for people with diabetes or anyone aiming to stabilize energy levels. Additionally, non-starchy vegetables are easier to add to meals without significantly increasing carbs, offering more dietary flexibility.
Health benefits of non-starchy vegetables
How they help in blood sugar control
Non-starchy vegetables have minimal impact on blood sugar due to their low carbohydrate content. The high fiber in these vegetables also slows the absorption of sugars, helping to prevent sudden spikes and drops in blood glucose. For people with diabetes or insulin resistance, incorporating non-starchy vegetables helps stabilize blood sugar, making them an ideal addition to every meal.
Role in weight management and satiety
Low in calories but high in fiber, non-starchy vegetables promote satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Because they take longer to digest, they can keep hunger at bay for longer periods, making them ideal for anyone aiming to lose or maintain weight.
Impact on digestion and gut health
Fiber-rich non-starchy vegetables support a healthy digestive system. Fiber aids in regular bowel movements, supports a healthy gut microbiome, and can reduce the risk of digestive disorders. Additionally, non-starchy vegetables contain antioxidants and phytonutrients that protect the cells lining the gut, promoting overall digestive health.
List of common non-starchy vegetables
Non-starchy vegetables come in a wide variety, each offering unique nutritional benefits. Here’s a breakdown of some popular non-starchy options:
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are high in vitamins A, C, and K.
- Cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts are known for their high fiber content and cancer-fighting compounds.
- Alliums: Onions, garlic, and leeks not only add flavor but also contain compounds that support immune function.
- Other common options: Bell peppers, cucumbers, and zucchini are low in calories and high in hydration, which can help keep the body hydrated and the skin healthy.
Incorporating non-starchy vegetables into daily meals
Tips for selection and meal prep
When buying non-starchy vegetables, opt for fresh, seasonal produce whenever possible, as it tends to be richer in nutrients. Frozen vegetables are also a great choice since they retain nutrients well. For meal prep, consider washing and cutting vegetables in advance to make them easier to add to meals throughout the week.
Creative ways to make them more appealing
There are countless ways to incorporate non-starchy vegetables creatively:
- Salads: Add a variety of greens and chopped vegetables for texture and flavor.
- Smoothies: Blend spinach or kale into a fruit smoothie for extra nutrients.
- Stir-fries: Toss a mix of vegetables in olive oil with garlic and ginger.
- Snacks: Slice cucumbers or bell peppers to enjoy with hummus or a low-fat dip.
Non-starchy vegetables for managing diabetes
For people managing diabetes, non-starchy vegetables are crucial. Their low-carb content ensures they don’t raise blood sugar levels, making them ideal for stabilizing glucose. For instance, pairing them with lean proteins or whole grains in meals can further minimize sugar spikes and provide lasting energy.
Importance in a diabetic diet
Incorporating non-starchy vegetables can help people with diabetes better manage their blood sugar. They provide essential vitamins and minerals that can sometimes be lacking in restricted diets and help reduce cravings for high-carb foods, making it easier to stick to a balanced meal plan.
Comparing starchy and non-starchy vegetables
Key differences in nutrients and effects on health
Starchy and non-starchy vegetables differ primarily in carbohydrate content. Starchy vegetables are higher in carbs, which break down into sugars in the body, leading to a faster release of glucose. In contrast, non-starchy vegetables have fewer carbs, making them less likely to affect blood sugar. Non-starchy options are also typically lower in calories and higher in water content, supporting hydration and weight management.
Frequently asked questions about non-starchy vegetables
Can non-starchy vegetables help with weight loss?
Yes, due to their low-calorie and high-fiber profile, non-starchy vegetables are excellent for weight management. They keep you feeling full and reduce the likelihood of overeating, making them a go-to choice for healthy weight loss.
How do they compare with low-carb vegetables?
While non-starchy vegetables are naturally low in carbs, not all low-carb vegetables are non-starchy. Non-starchy options like leafy greens, peppers, and cucumbers are low in both calories and carbs, making them ideal for low-carb diets.
Are they safe for children and pregnant women?
Absolutely. Non-starchy vegetables provide essential nutrients beneficial for all ages. For children, they support growth and development, while for pregnant women, they offer vital nutrients like folate, which supports fetal development.
Practical tips for buying and storing non-starchy vegetables
When purchasing non-starchy vegetables, look for vibrant colors and firm textures, as these often indicate freshness and nutrient richness. To extend shelf life, store vegetables in a cool, dry place, and consider blanching and freezing if you buy in bulk. Pre-chopping and storing them in airtight containers can also save time during the week, making it easier to add them to meals.